|

Understanding Knowledge Management
The Importance of Knowledge
§Resources of an organization must be protected, cultivated and shared among organization members to sustain continuity.
§To compete more effectively in the future an organization need to have the following elements such as Individual skills/competencies, thoughts, innovations and ideas
Problems Relating to Knowledge
§Usually exists in the minds of individuals
§Leaves the organization with the employee.
§Hidden in some forgotten report.
§People are not comfortable sharing what they know due to personal reason and organizational inhibitors.
§This is becoming an extremely expensive reality.
§Inefficiencies that result from intellectual work.
§Substandard performance
§The inability to find knowledge resources
§A better idea goes unused is a lost opportunity
Information becomes knowledge
Types of Knowledge
Tacit Knowledge
"highly personal and hard to formalize. Subjective insights, intuitions and hunches fall into this category of knowledge.”
E.g. Experience, Creativity, Skills, Innovation, etc.
Explicit Knowledge:
“can be expressed in words and numbers and can be easily communicated and shared in the form of hard data, scientific formulae, codified procedures or universal principles”
E.g. Pattern, R&D Materials, Best Practices, etc.
Knowledge Conversion – Tacit to Explicit

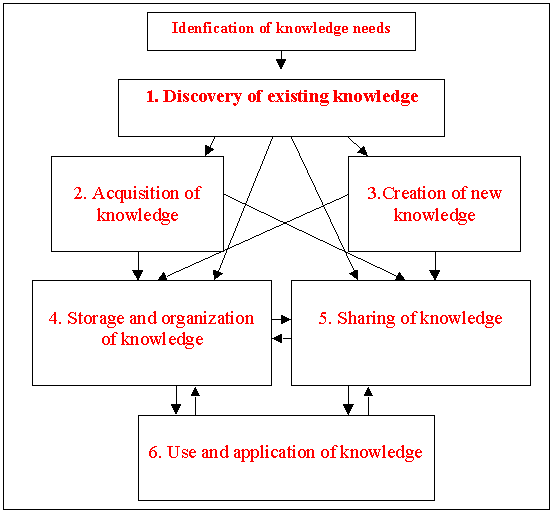
Overview of what is Knowledge Management

Source: http://informationr.net/ir/8-1/paper141.html
|