
Bengkel Knowledge Management Bil 1/2013
Bilik Siber 2 dan Makmal ISAC
IMATEC, INTAN Bukit Kiara, Kuala Lumpur
19 Mac hingga 22 Mac 2013
Objektif Kursus
1. Memberi pendedahan mengenai pengetahuan asas Pengurusan Pengetahuan
2. Meningkatkan pengetahuan peserta berkenaan pelaksanaan dan praktis Pengurusan Pengetahuan di agensi
3. Memberi pendedahan kepada Sistem Pengetahuan dan isu-isu berkaitan
“The illiterates of the 21st century will not be those who cannot read and write but
those who cannot learn, unlearn, and relearn”- Alvin Toffler ...
Day 1 19 Mac 2013 - Zakaria Deraman PPK IMATEC
Activity on Origami - Bird ....
a) in real working world, one who is not guided well enough tend not to finished his work due to the poor handling of
instructions by Head of Department
b) in the office normally, one who know much more better will have to keep their skill and knowledge to themselves as
others will claim for themselves for work that they did not do
c) knowledge is power, one who is learned tend to be much more better than the others
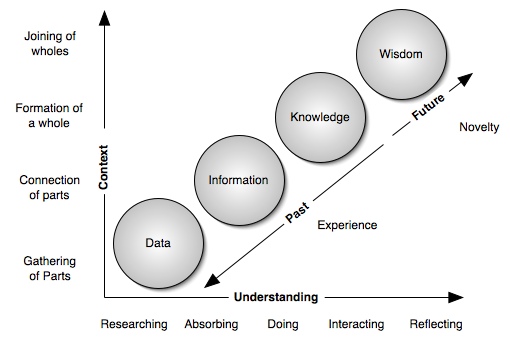
How Knowledge is Derived?
Data
•facts, numbers, images, sounds or individual entities without context
•simple observations of the world
Information
•comprises the basic facts with context and perspective
•relevance, purpose
•Information= data + interpretation
Knowledge
•the information which provides guidance for action or decision.
•valuable information from the human mind, includes reflection, synthesis, context
•Knowledge= information + use


Relations between data, information, knowledge and wisdom. Source: Adapted from Liebowitz, (2003)
Importance of Knowledge
To sustain continuity
To compete effectively on individual skills, competencies, thoughts, innovations and ideas
Problems relating to knowledge
Exist in minds of individuals
Not comfortable in organization
Substandard performance
Inability to find knowledge resource
Inefficiencies that result from intellectual work
Extremely expensive reality
Information becomes knowledge
When Conversation
When Consequences
When Connections
When Comparison
Dalam kehidupan hendaklah mesti menulis buku, sebagai panduan dan pedoman ......
Types of Knowledge
|
Tacit Knowledge
Explicit Knowledge
|
 |
|
The Nature of Knowledge
Explicit Knowledge – easier to replicate, contributes to efficiency, easier to document and share (10%)
Tacit Knowledge – leads to competency, harder to transfer, hard to articulate, skills and experience (90%)
|
|
Tacit
|
Tacit
|
|
|
Tacit
(You don't know)
|
Socialization
- brainstorming
- meeting santai
|
Externalization
- videotaping
- knowledge map
|
Explicit
|
|
Tacit
(You don't know)
|
Internalization
- training
- mentoring
|
Combination
- repositories
- CoP
|
Explicit
|
|
|
Explicit
(Knowledge you have)
|
Explicit
(Knowledge you don't have)
|
|
SECI Model Source: Ikujiro Nonaka
Knowledge Management Continuum